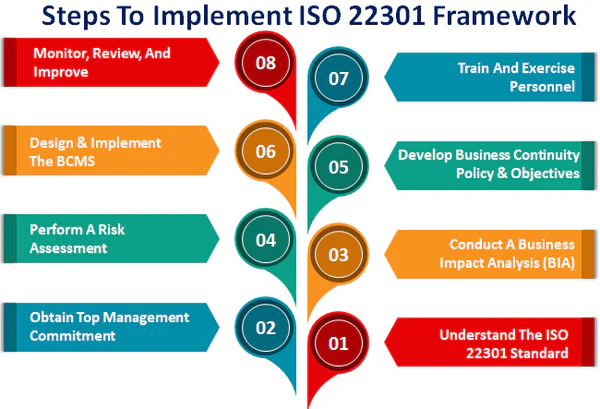
ISO 22301 is an international standard that sets out the requirements for business continuity management systems. It was published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in May 2012 and is the successor to BS 25999-2, which was developed by the British Standards Institution (BSI) in 2007. The current version of the standard is ISO 22301:2019 .
The ISO 22301 standard defines the requirements that business continuity management systems (BCMS) must meet to ensure that an organization can continue operating during and after crisis situations, such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, pandemics, armed conflicts or any other situation that may disrupt its activities.
ISO 22301 applies to any type of organization, regardless of size or sector. Business continuity management systems can be implemented by public or private companies, non-profit organizations, government institutions, and others.
Structure of the ISO 22301 standard
The ISO 22301 standard comprises 10 sections, which establish the requirements for Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS) for organizations. The sections of the ISO 22301 standard are detailed below:
- Purpose Here the scope of the organization’s BCMS is defined, specifying the processes, activities and areas that are included in the system.
- Normative references: This section includes an additional standard and related documents that are applicable to the SGCN.
- Terms and definitions: The terms and definitions used in ISO 22301 are broken down, ensuring that all parties involved in the BCMS use the same language and understand the same concepts.
- Organizational context: This section establishes the requirements for the organization to understand the context in which the BCMS operates, including legal, regulatory and contractual requirements, interested parties and the scope of the BCMS.
- Leadership: This section lists the requirements for senior management to assume responsibility for the implementation and maintenance of the BCMS, and to commit to providing the necessary resources, considering the continuity policy and the associated roles and responsibilities.
- Planning: This section sets out the requirements for planning the BCMS, including identifying BCMS risks and opportunities and defining objectives.
- Support: This section of the standard sets out the requirements for the support of the BCMS, including the provision of resources, communication, documentation, knowledge and competence.
- Operation : This section outlines the requirements for the implementation and operation of the SGCN, including conducting the Business Impact Analysis (BIA), risk analysis, mitigation measures, crisis management, and testing plans.
- Performance evaluation: This section indicates the requirements for the evaluation of the performance of the BCMS, including the measurement, analysis and evaluation of the effectiveness of the system and, finally, the performance of internal audit and management review of the system.
- Improvement: Finally, the steps to be followed for the continual improvement of the BCMS are listed here, including taking actions to address nonconformities, evaluating the effectiveness of the measures taken, and updating the BCMS.
Benefits of implementing ISO 22301 in companies
Implementing a business continuity management system based on the ISO 22301 standard offers several benefits for companies, including:
- Risk identification and assessment: The standard provides a framework for identifying and assessing risks that may affect an organization’s business continuity. This includes physical risks, such as earthquakes or fires, as well as cyber risks or supply chain-related risks.
- Crisis response planning: You will be able to establish the requirements for developing crisis response plans that allow the organization to respond quickly and effectively in case of emergencies.
- Implementation of mitigation measures: Based on the risk analysis conducted in the first point, mitigation measures will be implemented to minimize the impact of crisis situations and improve resilience.
- Maintaining business continuity: ISO 22301 establishes the requirements for maintaining business continuity during and after crisis situations. This includes implementing backup systems and recovery plans to ensure that the organization’s operations can continue in a degraded environment.
- Periodic testing: One of the keys when you have the BCMS implemented is the planned testing to verify that all continuity plans work correctly within the expected timeframes.
- Continuous improvement: Another benefit of implementing ISO 22301 is that it also establishes the requirements for evaluating and continuously improving the business continuity management system. This helps organizations adapt to changes in their environment and improve their resilience.
Companies with a business continuity management system based on ISO 22301 have a competitive advantage over organizations without such systems, as it allows them to be prepared to face crises and minimize the risks associated with business interruptions. It is an essential standard for any organization seeking to improve its crisis response capabilities, and its implementation helps organizations maintain business continuity and enhance the effectiveness of the system. Furthermore, it not only provides benefits to the organization but also helps improve its reputation by demonstrating its commitment to business continuity and its responsiveness to crises.
Why implement the standard using software?
Implementing a business continuity management system (BCMS) based on ISO 22301 can be a complex and challenging process. However, a software tool specifically designed for BCMS can simplify and streamline the implementation process, quickly improving the system’s effectiveness and efficiency with a user-centric approach.
Here are some reasons why it is advisable to implement the ISO 22301 standard with software:
- Process automation: Specialized software for the BCMS can automate many of the processes required for system implementation and maintenance. This includes automating documentation, risk management, incident management, and business continuity plans.
- Improved efficiency: Automating processes can improve the efficiency of implementing the BCMS, allowing resources to focus on other important tasks.
- Greater accuracy: Automating processes can improve the accuracy of the information handled in the BCMS, allowing for better decision-making.
- Enhanced security: Specialized software for the NCMS can improve information security, preventing confidential and sensitive data from being lost or compromised.
- Improved collaboration: Specialized software for the BCMS can improve collaboration between different departments of the organization, facilitating the exchange of information and decision-making.
- Complete traceability: The tool provides tracking across processes, assets, BIA, risk analysis, strategies, plans, and tests to ensure that everything is fully considered in the BCMS.
- Ease of auditing: The use of specialized software for the BCMS can facilitate the auditing of the system, allowing for better documentation and monitoring of the measures taken.
Read More ISO 27001